
Função do tensor da fáscia lata Pacientes do Dr. Márcio Silveira, Ortopedista em Brasília / DF
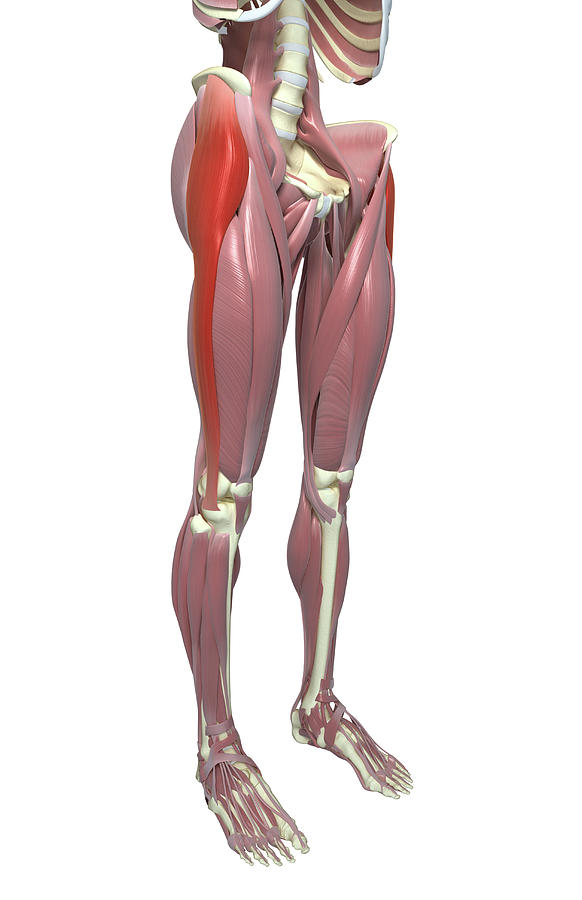
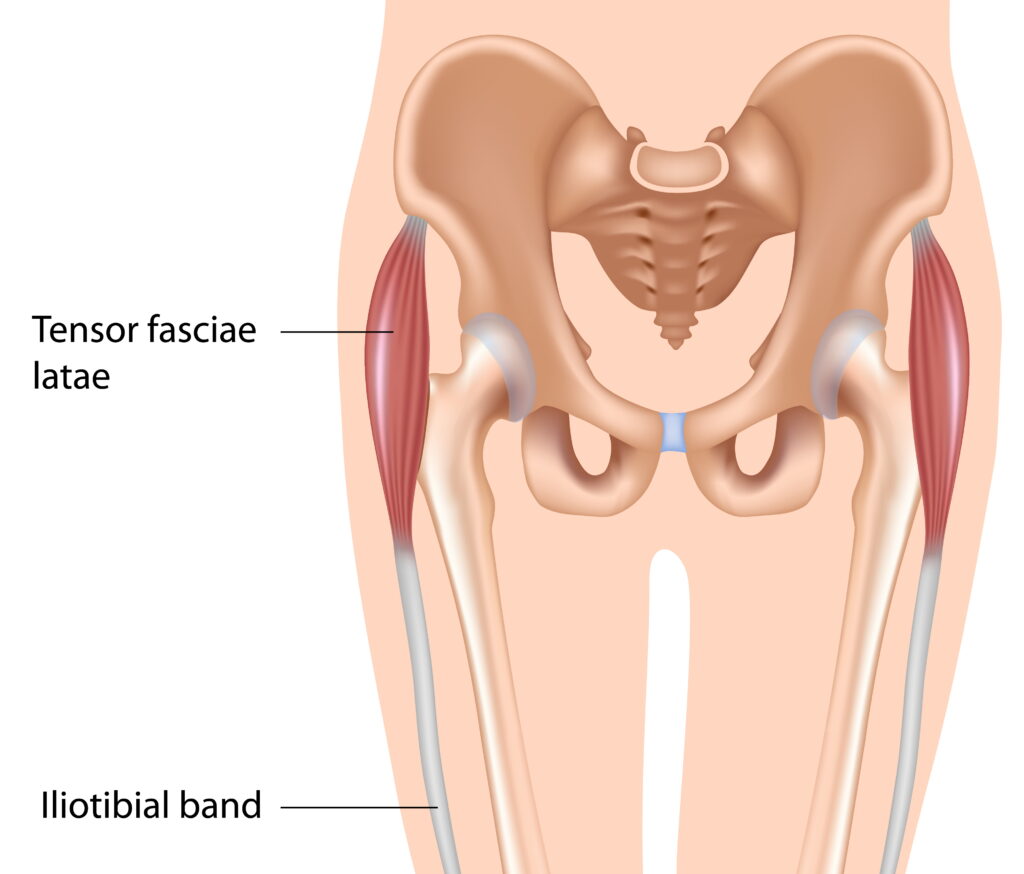
The tensor fasciae latae (or tensor fasciæ latæ or, formerly, tensor vaginae femoris) is a muscle of the thigh. Together with the gluteus maximus, it acts on the iliotibial band and is continuous with the iliotibial tract, which attaches to the tibia. The muscle assists in keeping the balance of the pelvis while standing, walking, or running.
Tensor Fasciae Latae by
Tensor fasciae latae is latin for tense band side. It describes the function and location of the muscle. The TFL tenses the iliotibial (IT) band at the side of your body. The TFL is a thigh muscle that helps maintain pelvic balance while standing, walking, or running. It acts on the iliotibial band along with the gluteus maximus and is.

Tensor fascia latae unraveling the mysteries
The tensor fascia latae or singular version of tensor fascia lata is often forgotten about, but it plays a vital role in hip function. When the Tensor Fascia Latae (TFL) is tight, it can wreak havoc on your body. A tight TFL can lead to knee pain, groin pain, and hip problems. If you are an athlete, it is especially important that you keep this.
Tensor fasciae latae pain common cause of hip pain in runners
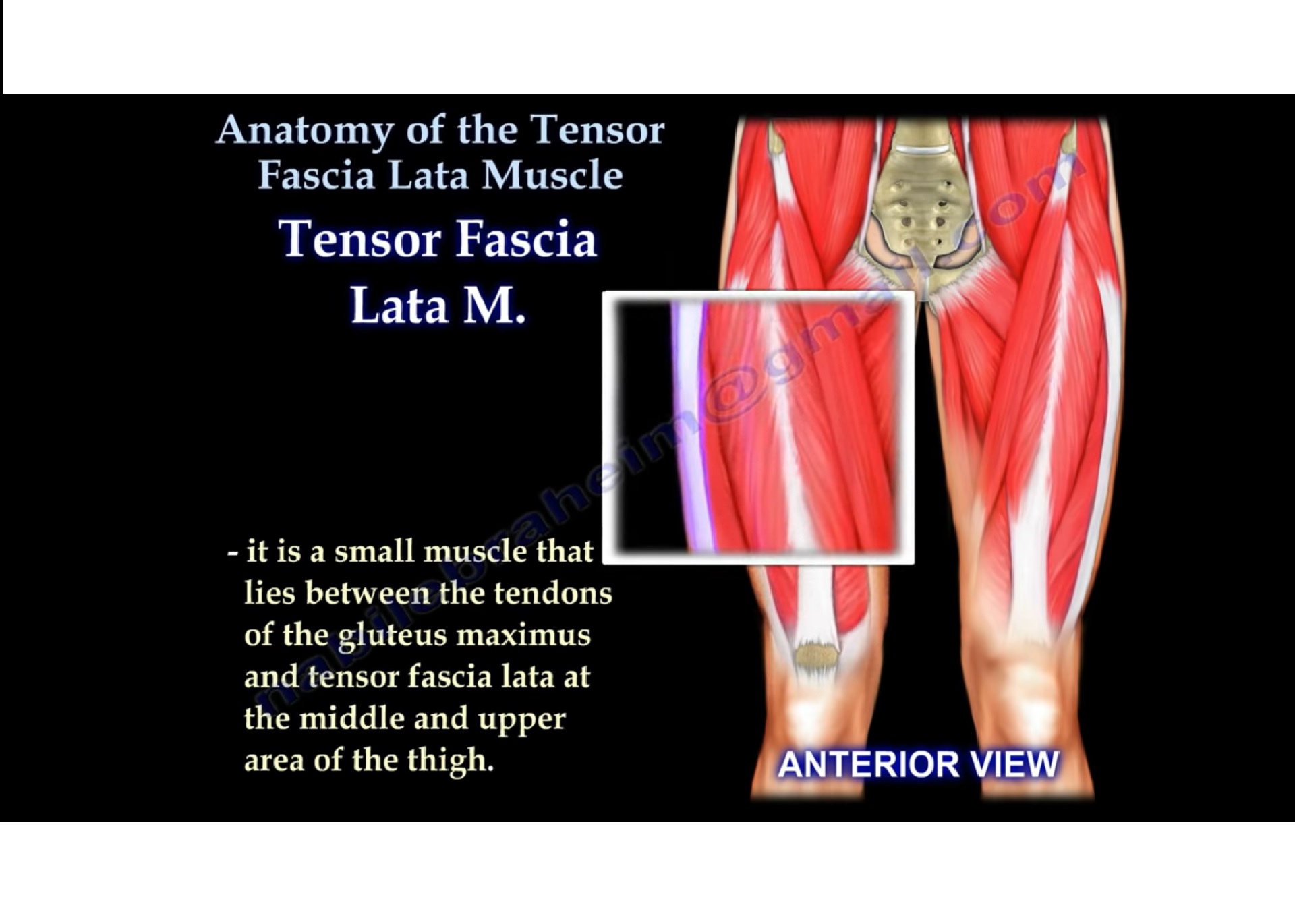
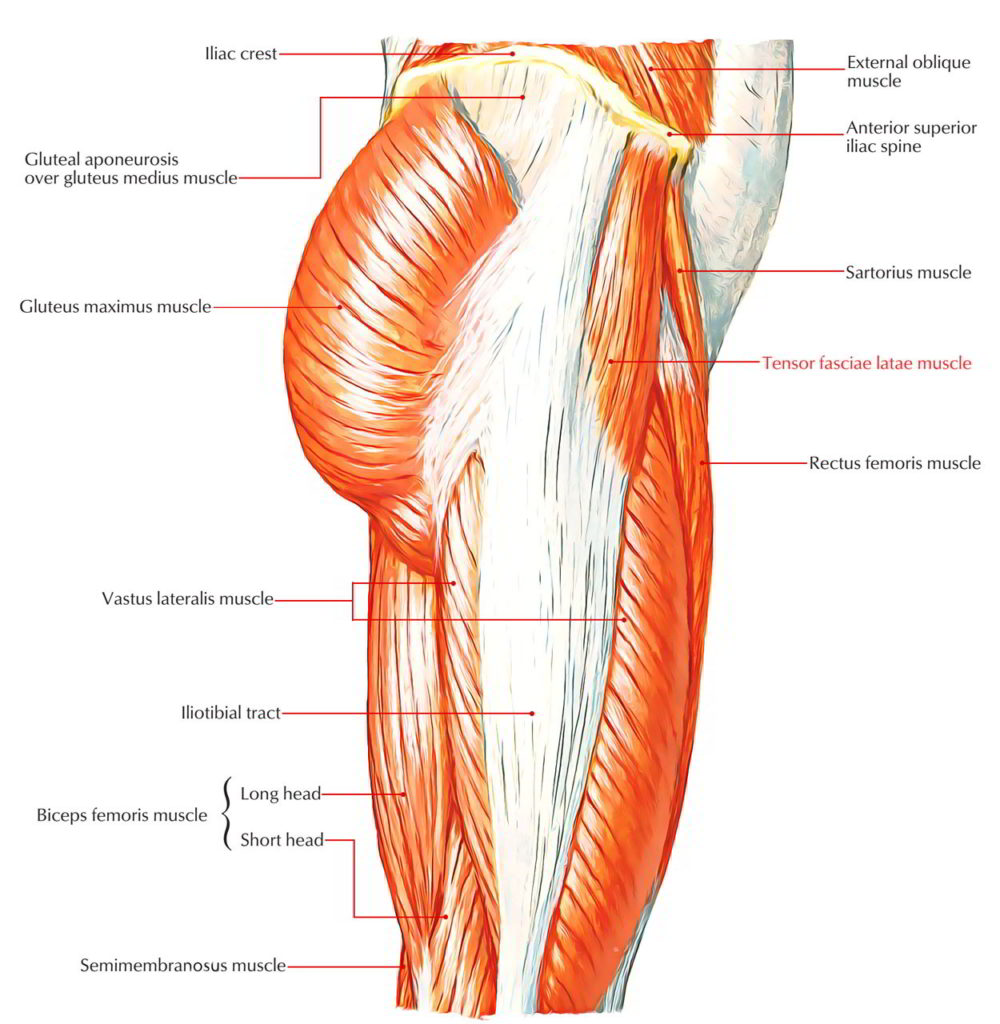
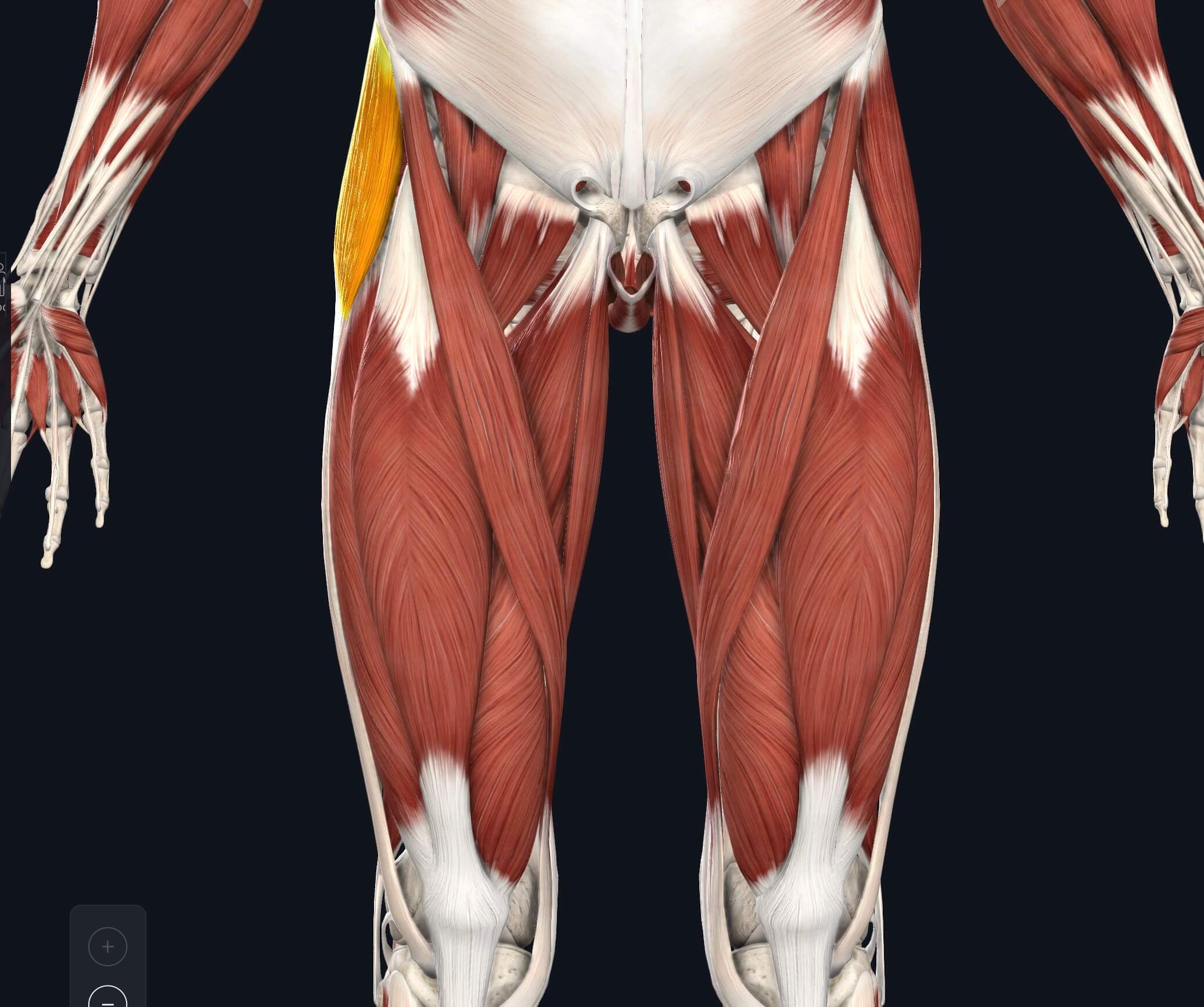
The tensor fasciae latae muscle is the most superficial muscle of the anterolateral aspect of the thigh. It is positioned lateral to the hip joint, immediately beneath the skin.In its superior aspect, tensor fasciae latae is found between the sartorius and gluteus medius muscle, where it overlays the gluteus minimus muscle. While descending down the thigh, the muscle is found between the two.
Tensor Fascia Lata —
In this video, we explore the anatomy of the tensor fascia lata (TFL) muscle by discussing its origin, insertion, and other relevant clinical features.INSTAG.
Tensor Fasciae Latae Earth's Lab
The tensor fasciae latae (TFL) is a muscle of the proximal anterolateral thigh that lies between the superficial and deep fibres of the iliotibial (IT) band.There is high variability in muscle belly length, although, in most patients, the TFL muscle belly ends before the greater trochanter of the femur.The TFL muscle is about 15cm in length.. The TFL works in conjunction with the gluteus.
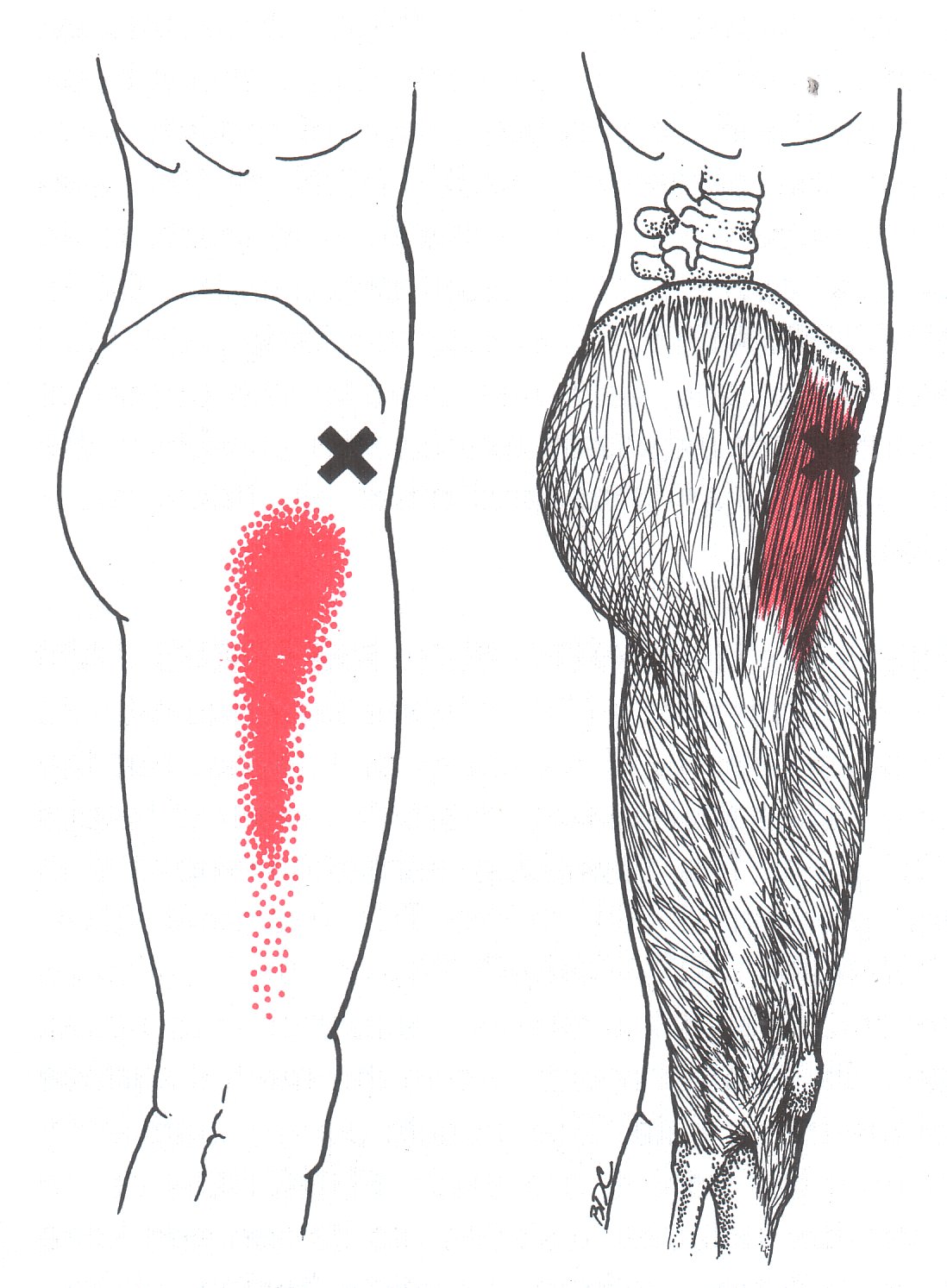
Tensor Fasciae Latae The Trigger Point & Referred Pain Guide
When stimulated, the tensor fasciae lata tautens the iliotibial band and braces the knee, especially when the opposite foot is lifted. The property of TFL tightening the fascia lata is analogous to hoisting an elastic stocking up the thigh. When the fascia lata is pulled taut, it forces muscles in the anterior and posterior compartments closer.

Tensor Fasciae Latae (TFL) Learn Muscles
The tensor fasciae latae is a tiny muscle, inferior to the iliotibial band. This band, also called the IT band, is an elongated strip of fascia — a type of connective tissue — located in the.
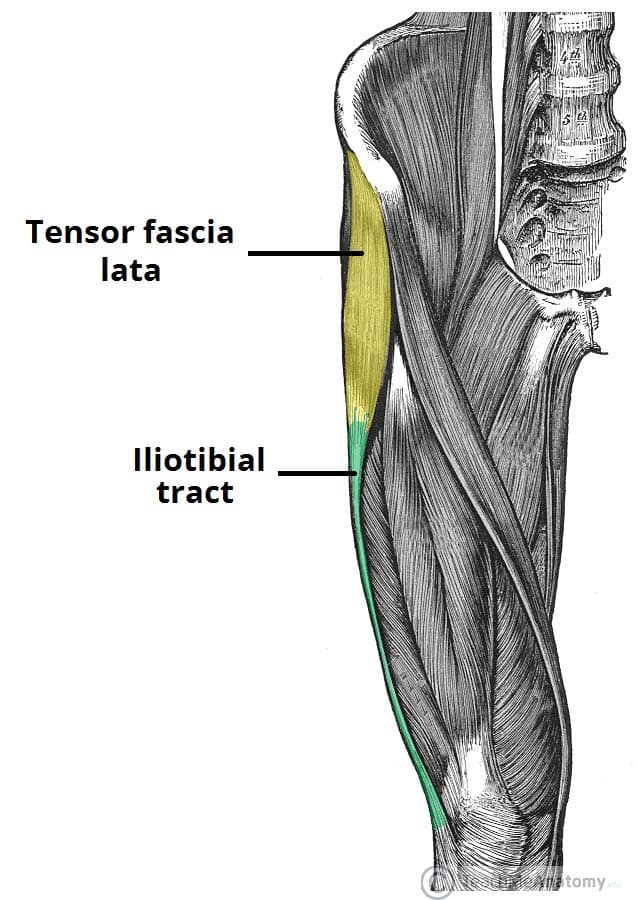
The Fascia Lata Structure Iliotibial Tract TeachMeAnatomy
The tensor fasciae latae (TFL) is a muscle of the proximal anterolateral thigh that lies between the superficial and deep fibers of the iliotibial (IT) band. There is high variability in muscle belly length, although, in most patients, the TFL muscle belly ends before the greater trochanter of the femur. The TFL works in conjunction with the gluteus maximus, gluteus medius, and gluteus minimus.

tensorfascialata Esculpe tu cuerpo
5 tensor fasciae latae exercises to reduce over-activity The TFL is a small workhorse of a muscle that can become overused. Because of this reason it's important to perform strengthening exercises that activate the neighboring hip abductor muscles, the gluteus minimus and gluteus medius while reducing the load on the TFL.

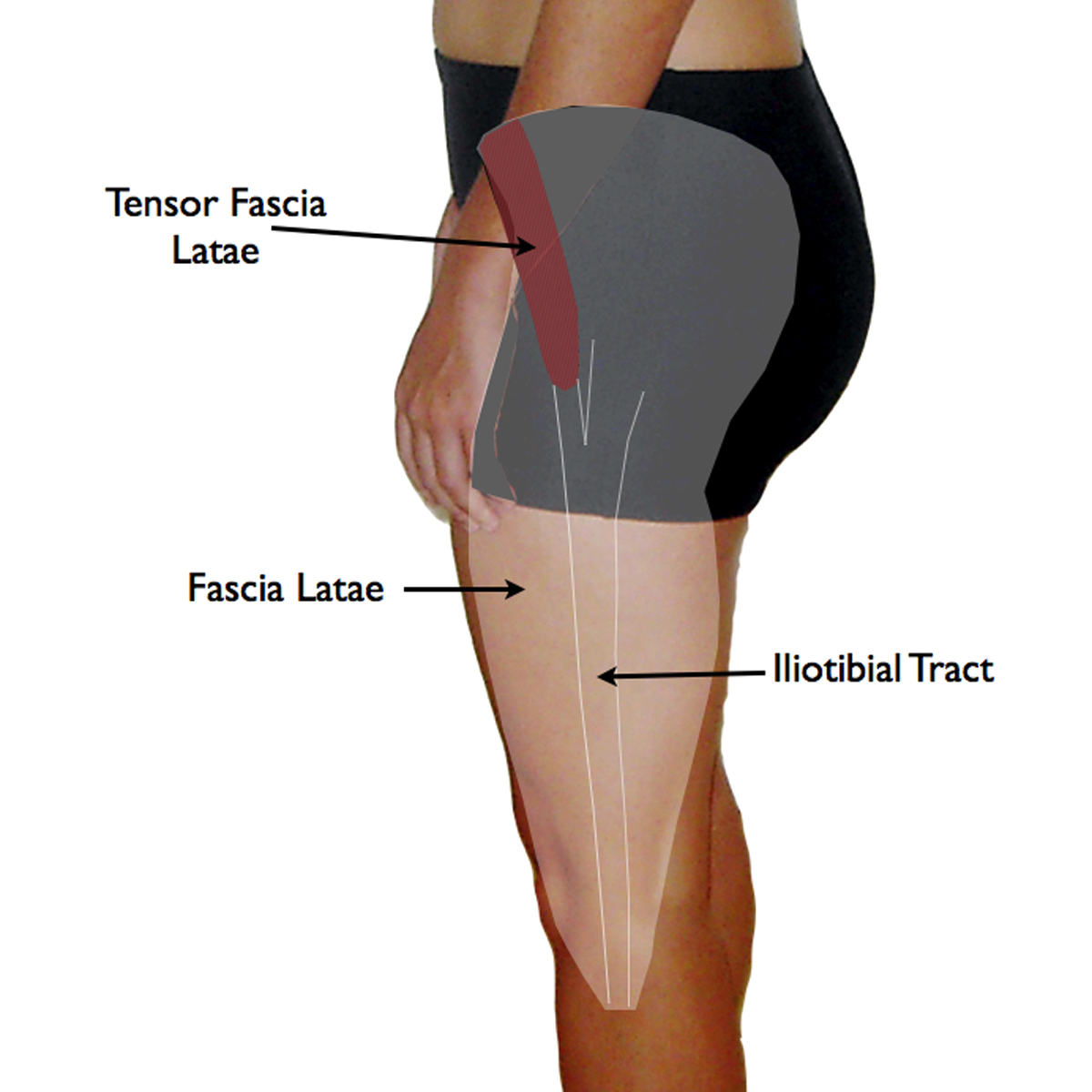
Tensor Fascia Latae and the Iliotibial Band
The tensor fascia lata is a muscle of the gluteal region in the lower limb. It is a small superficial muscle which lies towards the anterior edge of the iliac crest. It functions to tighten the fascia lata, and so abducts and medially rotates the lower limb. Attachments: Originates from the anterior iliac crest, attaching to the anterior.
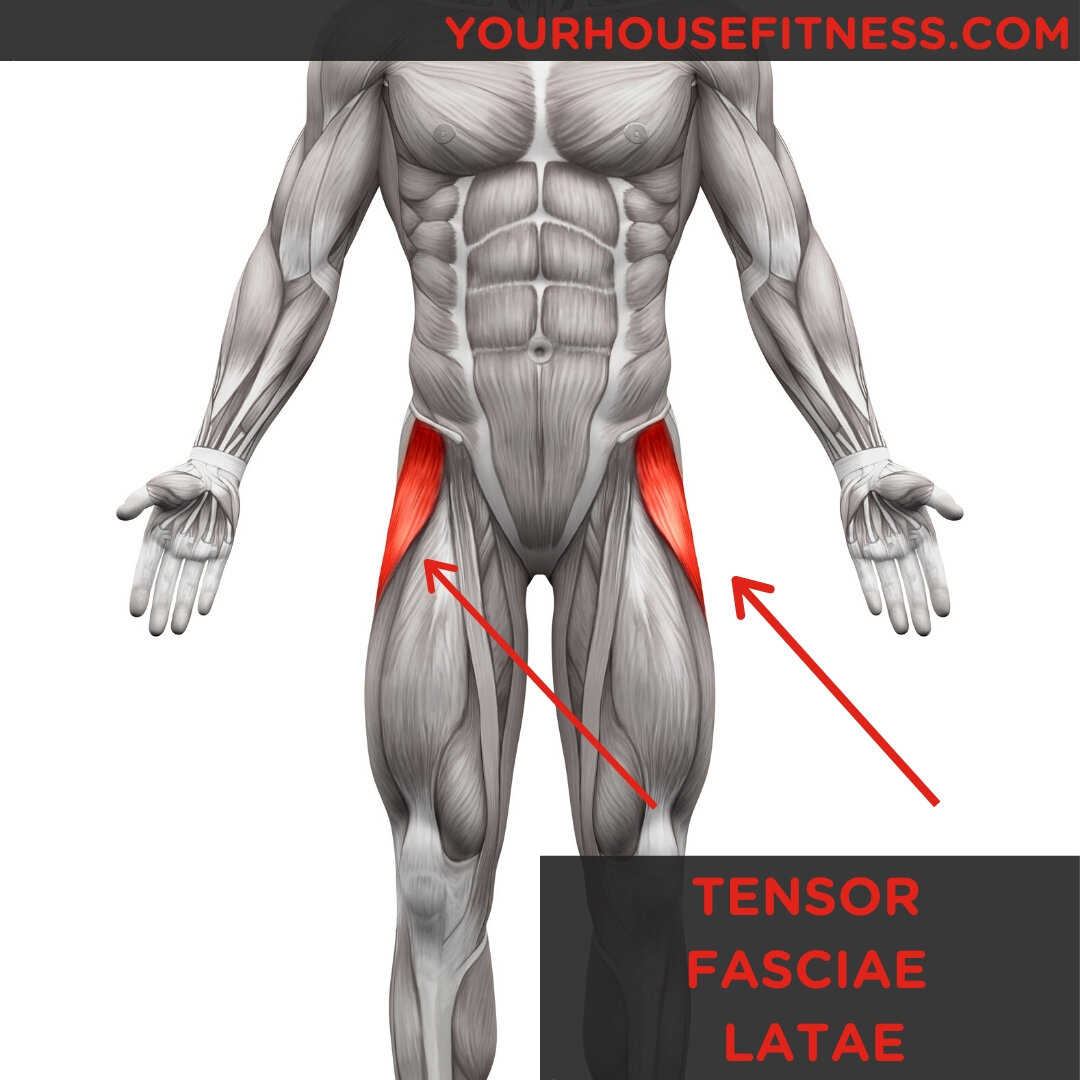
Muscle Breakdown Tensor Fasciae Latae
The tensor fasciae latae originates just behind (posterior) or to the outside of the anterior superior iliac spine or ASIS. Insertion. Tensor fascia latae inserts on the iliotibial band. Tensor fascia latae is one of two muscles that insert onto the iliotibial band. The other muscle that inserts onto the iliotibial band is the gluteus maximus.
Tensor Fascia Lata Trigger Point in IT Band and Hip Pain Complaints
Tensor Fasciae Latae, otherwise known by its abbreviation TFL, is a thin muscle of the hip region located on the thigh just inferior and lateral to the anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS).Despite its small size, the TFL is largely important with a number of functions, including hip abduction, internal rotation, and hip flexion.

Tensor Fascia Latae Muscle and the Iliotibial Band Yoganatomy
An injury to the tensor fasciae latae causes pain at the TFL muscle and into the upper leg. TFL tightness often contributes to iliotibial band syndrome. IT band syndrome also causes pain on the outside of the thigh. TFL overuse causes tight spots (called trigger points) to form in the muscle. Trigger points in the TFL cause pain down the side.
Stretching Tensore della fascia lata come farlo in modo corretto (VIDEO)
The name tensor fasciae latae may sound like it's from a different language and, well, that's because it is. It's from latin and translates to "stretcher of the wide band" [1] . Tensor means stretcher and the wide band in this case is the fasciae lata, which is the fascia that surrounds all of the thigh muscles.
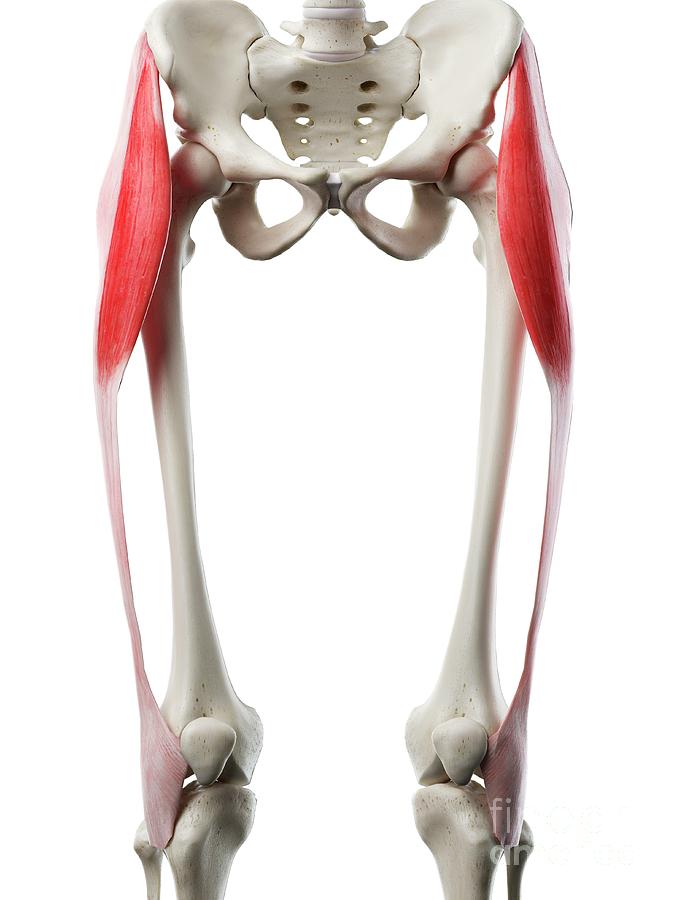
Tensor Fascia Lata Muscle Photograph by Sebastian Kaulitzki/science Photo Library Pixels
Synonyms: none. The fascia lata, or the deep fascia of the thigh, is an especially strong fascial sheath which envelops the thigh like a sleeve. Lata is Latin for 'broad' meaning that this fascia encloses a wide area of the thigh region. The fascia lata wraps the large muscles of the thigh and forms the outer limit of the fascial compartments.